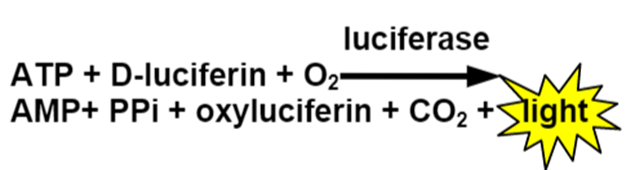
All living cells contain ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and when the cell dies ATP is degraded by intracellular enzymes to ADP and finally AMP. The intracellular ATP concentration is similar in different cell types. Bacterial cells contain 1-2 attomoles per cell while animal and plant cells contain 100 to 10 000 times as much ATP.
Extracellular ATP may be degraded by adding ATP consuming enzymes or by physical separation. Determination of intracellular ATP can then be used to estimate biomass. If the amount of ATP per cell is known the cell number may also be estimated.
In sample which likely contains urine, extracellular ATP, ATP in somatic cells and ATP in bacterial cells all three ATP pools can be determined.